


Next: BBA Results
Up: Beam-Based-Alignment (BBA)
Previous: Beam-Based-Alignment (BBA)
The applied method [4,5] is based on the well known fact that if the strength
of a single quadrupole 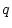 in the ring is changed, the resulting
difference in the closed orbit
in the ring is changed, the resulting
difference in the closed orbit 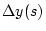 is
proportional to the original offset
is
proportional to the original offset 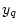 of the beam at
of the beam at 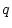 .
.
The equation for the resulting difference orbit is:
The difference orbit is thus given by the closed orbit formula
for a single kick, but calculated with the perturbed optics
including 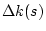 .
.
Figure 2:
Illustration of the beam-based alignment technique applied
to the quadrupoles with adjacent BPMs
|
|
From the measured difference orbit
the kick and thus 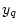 can be easily determined and compared
to the nominal orbit
can be easily determined and compared
to the nominal orbit 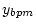 in the BPM adjacent to the quadrupole,
yielding the offset between BPM and quadrupole axis.
The precision of the method is very much improved by taking
difference orbit data for several local beam positions
in the BPM adjacent to the quadrupole,
yielding the offset between BPM and quadrupole axis.
The precision of the method is very much improved by taking
difference orbit data for several local beam positions 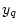 varied
with an orbit bump. The principle of the method is illustrated in
Fig. 2.
The error of the nominal position
varied
with an orbit bump. The principle of the method is illustrated in
Fig. 2.
The error of the nominal position 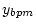 for
which the beam goes through the center of the quadrupole is then given
by the resolution of the BPM system. In the SLS storage ring,
a difference orbit with an amplitude of 5
for
which the beam goes through the center of the quadrupole is then given
by the resolution of the BPM system. In the SLS storage ring,
a difference orbit with an amplitude of 5 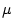 m can be clearly resolved [6]. This results in a resolution for the local kick of
m can be clearly resolved [6]. This results in a resolution for the local kick of 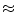 0.25
0.25 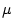 rad for quadrupoles at vertical beta values of 20 m. Since a change in quadrupole strength of
rad for quadrupoles at vertical beta values of 20 m. Since a change in quadrupole strength of 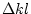 = 0.02 m
= 0.02 m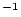 causing a tune variation
causing a tune variation 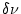 = 0.03, is possible without losing the beam, a minimum beam offset of
= 0.03, is possible without losing the beam, a minimum beam offset of 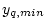 = 15
= 15 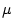 m can be easily detected. Taking several
data points by varying a local bump, the quadrupole-to-BPM alignment can be done with a precision of
m can be easily detected. Taking several
data points by varying a local bump, the quadrupole-to-BPM alignment can be done with a precision of 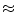 5
5 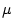 m. However some of the quadrupoles are at low beta values of 2.5 m which reduces the precision of the measurement to
m. However some of the quadrupoles are at low beta values of 2.5 m which reduces the precision of the measurement to 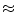 40
40 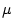 m.
m.



Next: BBA Results
Up: Beam-Based-Alignment (BBA)
Previous: Beam-Based-Alignment (BBA)
Michael Boege
2002-06-19
![\includegraphics [width=1.1\linewidth=3.0]{WEPLE007f2.eps}](img29.gif)